Hacking APT Team Tools
Autorius: #0409HACKEDofBaltic Šaltinis: https://leadsblue.com/leads/li... 2023-09-06 18:31:00, skaitė 567, komentavo 1

Cellular Network Antennas and Civil Defense Sirens for Geolocation
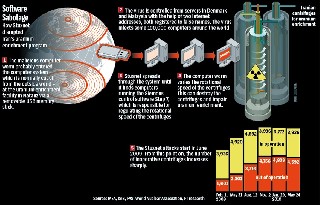
What is Stuxnet? First of all, this piece of malware had to be named. Since no one came out to tell it’s their creation, and there was no clear understanding of its purpose, experts analyzed the code and, among the binary numbers, found two phrases: “stub” and “xnet”, thus combining it into Stuxnet. By definition, Stuxnet is a malicious computer worm. It is designed to infect specific devices, replicate itself, and cause damage.
Regarding its origins, no one can be absolutely sure, but a safe guess is that it’s a joint effort of American-Israeli forces. The political landscapes are self-explanatory, the tensions between the west and the Middle East are, sadly, still ongoing, and the US expressed their frustrations regarding Iran’s nuclear program many times.
Another argument is that it’s unlikely that any hacker group or community would have the resources to develop such a sophisticated worm. According to the report by report by Symantec, the development “full cycle may have taken six months and five to ten core developers not counting numerous other individuals, such as quality assurance and management.” And since Stuxnet has no features to extract monetary value, it’s a safe assumption that a nation-state is behind it.
Last, but not least, Stuxnet exploited the same vulnerabilities that were used for Flame malware, and the knowledge of these zero-day vulnerabilities are linked to the Equation group, a semi-secret American organization, dubbed by the same Kaspersky lab as “the most advanced” cyber attack groups. All these are just assumptions and logical conclusions, without any facts whatsoever. And that must be taken into consideration, because Stuxnet is much more than just a simple worm.
1. Introduction:Stuxnet
2. Stuxnet Worm Source Code
3. Decompilation of Stuxnet.
Canarytokens free tool
CVE-2019-11510 Exploit for Arbitrary File Read on Pulse Secure SSL VPN (CVE-2019-11510) https://github.com/projectzeroindia/CVE-2019-11510
CVE-2020-5902 exploit code for F5-Big-IP (CVE-2020-5902) https://github.com/yasserjanah/CVE-2020-5902
CVE-2019-19781 A Citrix Application Delivery Controller (ADC) and Gateway directory traversal vulnerability, which can lead to remote code execution without credentials. https://github.com/projectzeroindia/CVE-2019-19781
CVE-2020-8193-Citrix-Scanner - https://github.com/PR3R00T/CVE-2020-8193-Citrix-Scanner
Citrix_adc_netscaler_lfi_scan - https://github.com/Zeop-CyberSec/citrix_adc_netscaler_lfi
CVE-2019-0708 - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in Remote Desktop Services https://github.com/CVE-2019-0708/CVE-2019-0708
CVE-2020-15505 - https://github.com/iamnoooob/CVE-Reverse/tree/master/
CVE-2020-15505 Exploit Active Directory for Lateral Movement and Credential Access: CVE-2020-1472 Checker & Exploit Code for CVE-2020-1472 aka Zerologon https://github.com/VoidSec/CVE-2020-1472
CVE-2019-1040 scanner Checks for CVE-2019-1040 vulnerability over SMB. The script will establish a connection to the target host(s) and send an invalid NTLM authentication. https://github.com/fox-it/cve-2019-1040-scanner
Exploit public-facing servers: Attackers use these vulnerabilities to bypass authentication in web servers, email servers, or DNS to remotely execute commands on the internal network.
For compromised web servers, attackers can utilize them in watering-hole attacks to target future visitors. CVE-2020-1350 The Windows DNS server SigRed vulnerability allows attackers to spread laterally through a network. https://github.com/ZephrFish/CVE-2020-1350
CVE-2018-6789 Exim CVE-2018-6789 PoC materials to exploit CVE-2018-6789. https://github.com/synacktiv/Exim-CVE-2018-6789
CVE-2018-4939 https://nickbloor.co.uk/2018/06/18/another-coldfusion-rce-cve-2018-4939/
Exploit internal servers: These vulnerabilities are used to spread laterally throughout a network and gain access to internal servers, where the attackers can steal valuable data.
CVE-2020-0688 - A Microsoft Exchange vulnerability that allows authenticated users to perform remote code execution https://github.com/ravinacademy/CVE-2020-0688
CVE-2015-4852 - The WLS Security component in Oracle WebLogic15 Server allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands via a crafted serialized Java16 object. https://github.com/roo7break/serialator
CVE-2020-2555 - A vulnerability exists in the Oracle® Coherence product of Oracle Fusion® Middleware. This easily exploitable https://github.com/Y4er/CVE-2020-2555
CVE-2019-3396 - A server-side template injection vulnerability is present in the Widget Connector in Atlassian Confluence servers that allows remote attackers to perform remote code execution and path traversal. https://github.com/jas502n/CVE-2019-3396
CVE-2019-11580 - Attackers who can send requests to an Atlassian® Crowd or Crowd Data Center instance can exploit this vulnerability to install arbitrary plugins, permitting remote code execution. This vulnerability was used in GandCrab ransomware attacks in the past. https://github.com/jas502n/CVE-2019-11580
Invoke-DNSteal - Simple And Customizable DNS Data Exfiltrator Invoke-DNSteal
CVE-2019-18935 - A vulnerability in Telerik 19 UI for ASP.NET AJAX can lead to remote code execution. It was seen used by a hacker group named 'Blue Mockingbird' to install Monero miners on vulnerable servers but could be used to spread laterally as well. https://github.com/noperator/CVE-2019-18935
Exploit secure remote access: To gain access to networks, APT threat actors utilize seven different vulnerabilities, many of which also provide credentials that can be used to spread further on the network. #0409HACKEDofBaltic